The Connection Between Balance and Hearing
Many people do not realize that the ears are responsible for more than

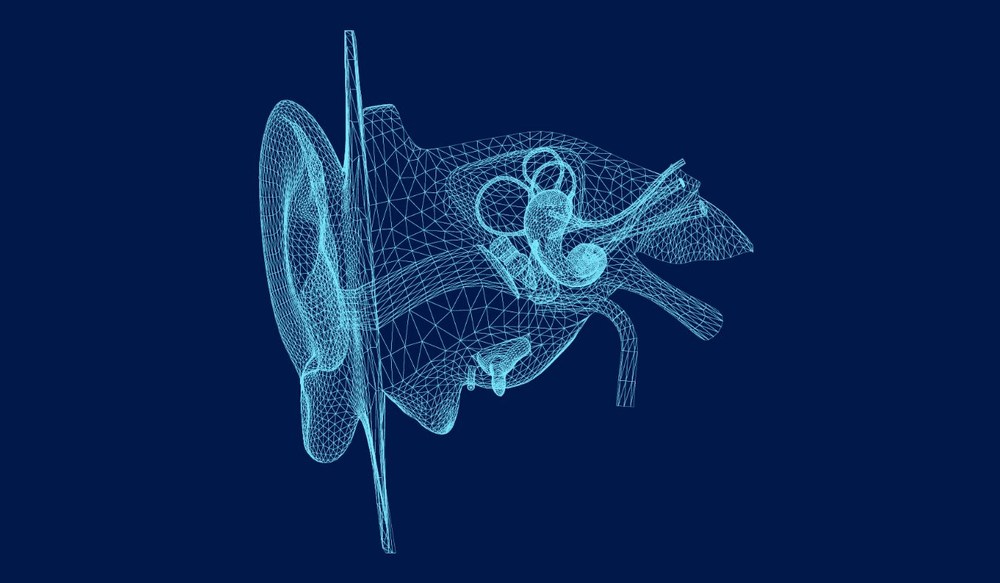
Many people do not realize that the ears are responsible for more than

When you buy hearing aids, it’s important to pay attention to the
When it comes to hearing aids, one common question is whether wearing a